Item Description
2.5″ British Sort Fire Hose Coupling in Hearth Combating
Transient Description
A hose coupling is a connector on the end of a hose to hook up or pair it with another hose orwith a faucet or a hose equipment, such as an irrigation sprinkler. It is generally madeof steel, brass, stainless metal, aluminium or plastic. Employed for combining water band with waterband ,fire hydrant ,h2o lance and the fire-preventing truck so that they are to source drinking water orfoam misture for putting out fireplace.
Our principal creation line for hose coupling is KD,KN,KY,KWA,KWS ect for fireplace hose coulping through electrophoretic technique,so that our product can be anti-corrosion.
Specialized Specification
| Fire Hose Coupling Sort | Inlet | Outlet |
| British/John Morris Coupling |
two.5″BS336 | Φ63.5 |
| two”BS336 | Φ51 | |
| 1.5″BS336 | Φ38 | |
| two.5″BS336 | Φ51 | |
| two.5″BS336 | Φ38 | |
| two”BS336 | Φ38 |
| Hearth Hose Coupling Type | Inlet | Outlet |
| American(ANSI Pin)Hearth Hose Coupling |
2.5″NH | Φ63.five |
| 2″NH | Φ51 | |
| one.5″NH | Φ38 |
| Fireplace Hose Coupling Type | Inlet | Outlet |
| Nakajima(Machino) fire hose coupling |
2.5″ | Φ63.five |
| two” | Φ51 | |
| 1.5″ | Φ38 |
| Fireplace Hose Coupling Variety | Inlet | Outlet |
| Forestry Fireplace Hose Coupling |
one.5″ | Φ38 |
| 1.5″ | one.5″ BSP | |
| one.5″ | one.5″ NPSH | |
| one.5″ | F1.5″ BSP |
| Fireplace Hose Coupling Kind | Inlet | Outlet |
| Gost(Russian) Fireplace Hose Coupling |
two” | Φ50 |
| two.5″ | Φ70 | |
| three” | Φ80 | |
| four” | Φ100 |
| Fire Hose Coupling Variety | Inlet | Outlet |
| UNI Hearth Hose Coupling | UNI70 | Φ70 |
| UNI45 | Φ45 |
| Hearth Hose Coupling Type | Inlet | Outlet |
| Storz Fire Hose Coupling |
four” STORZ | Φ100 |
| three” STORZ | Φ75.five | |
| two.5″ STORZ | Φ63.five | |
| two” STORZ | Φ51 | |
| 1 3/4″ STORZ | Φ44.five | |
| 1″ STORZ | Φ38 |
Photoes
| To Be Negotiated | 50 Pieces (Min. Order) |
###
| Certification: | CCCF, ISO |
|---|---|
| Surface Treatment: | Chrome Plated/Brass |
| Material: | Aluminium/Brass |
| Transport Package: | Bags/Cartons |
| Specification: | 1.5"-2.5" |
| Trademark: | GW/OEM |
###
| Samples: |
US$ 0.1/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) |
|---|
###
| Customization: |
Available
|
|---|
###
| Fire Hose Coupling Type | Inlet | Outlet |
| British/John Morris Coupling |
2.5"BS336 | Φ63.5 |
| 2"BS336 | Φ51 | |
| 1.5"BS336 | Φ38 | |
| 2.5"BS336 | Φ51 | |
| 2.5"BS336 | Φ38 | |
| 2"BS336 | Φ38 |
###
| Fire Hose Coupling Type | Inlet | Outlet |
| American(ANSI Pin)Fire Hose Coupling |
2.5"NH | Φ63.5 |
| 2"NH | Φ51 | |
| 1.5"NH | Φ38 |
###
| Fire Hose Coupling Type | Inlet | Outlet |
| Nakajima(Machino) fire hose coupling |
2.5" | Φ63.5 |
| 2" | Φ51 | |
| 1.5" | Φ38 |
###
| Fire Hose Coupling Type | Inlet | Outlet |
| Forestry Fire Hose Coupling |
1.5" | Φ38 |
| 1.5" | 1.5" BSP | |
| 1.5" | 1.5" NPSH | |
| 1.5" | F1.5" BSP |
###
| Fire Hose Coupling Type | Inlet | Outlet |
| Gost(Russian) Fire Hose Coupling |
2" | Φ50 |
| 2.5" | Φ70 | |
| 3" | Φ80 | |
| 4" | Φ100 |
###
| Fire Hose Coupling Type | Inlet | Outlet |
| UNI Fire Hose Coupling | UNI70 | Φ70 |
| UNI45 | Φ45 |
###
| Fire Hose Coupling Type | Inlet | Outlet |
| Storz Fire Hose Coupling |
4" STORZ | Φ100 |
| 3" STORZ | Φ75.5 | |
| 2.5" STORZ | Φ63.5 | |
| 2" STORZ | Φ51 | |
| 1 3/4" STORZ | Φ44.5 | |
| 1" STORZ | Φ38 |
| To Be Negotiated | 50 Pieces (Min. Order) |
###
| Certification: | CCCF, ISO |
|---|---|
| Surface Treatment: | Chrome Plated/Brass |
| Material: | Aluminium/Brass |
| Transport Package: | Bags/Cartons |
| Specification: | 1.5"-2.5" |
| Trademark: | GW/OEM |
###
| Samples: |
US$ 0.1/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) |
|---|
###
| Customization: |
Available
|
|---|
###
| Fire Hose Coupling Type | Inlet | Outlet |
| British/John Morris Coupling |
2.5"BS336 | Φ63.5 |
| 2"BS336 | Φ51 | |
| 1.5"BS336 | Φ38 | |
| 2.5"BS336 | Φ51 | |
| 2.5"BS336 | Φ38 | |
| 2"BS336 | Φ38 |
###
| Fire Hose Coupling Type | Inlet | Outlet |
| American(ANSI Pin)Fire Hose Coupling |
2.5"NH | Φ63.5 |
| 2"NH | Φ51 | |
| 1.5"NH | Φ38 |
###
| Fire Hose Coupling Type | Inlet | Outlet |
| Nakajima(Machino) fire hose coupling |
2.5" | Φ63.5 |
| 2" | Φ51 | |
| 1.5" | Φ38 |
###
| Fire Hose Coupling Type | Inlet | Outlet |
| Forestry Fire Hose Coupling |
1.5" | Φ38 |
| 1.5" | 1.5" BSP | |
| 1.5" | 1.5" NPSH | |
| 1.5" | F1.5" BSP |
###
| Fire Hose Coupling Type | Inlet | Outlet |
| Gost(Russian) Fire Hose Coupling |
2" | Φ50 |
| 2.5" | Φ70 | |
| 3" | Φ80 | |
| 4" | Φ100 |
###
| Fire Hose Coupling Type | Inlet | Outlet |
| UNI Fire Hose Coupling | UNI70 | Φ70 |
| UNI45 | Φ45 |
###
| Fire Hose Coupling Type | Inlet | Outlet |
| Storz Fire Hose Coupling |
4" STORZ | Φ100 |
| 3" STORZ | Φ75.5 | |
| 2.5" STORZ | Φ63.5 | |
| 2" STORZ | Φ51 | |
| 1 3/4" STORZ | Φ44.5 | |
| 1" STORZ | Φ38 |
Types of Couplings
A coupling is a device used to join two shafts together and transmit power. Its purpose is to join rotating equipment while permitting a degree of end movement and misalignment. There are many types of couplings, and it is important to choose the right one for your application. Here are a few examples of couplings.
Mechanical
The mechanical coupling is an important component in power transmission systems. These couplings come in various forms and can be used in different types of applications. They can be flexible or rigid and operate in compression or shear. In some cases, they are permanently attached to the shaft, while in other cases, they are removable for service.
The simplest type of mechanical coupling is the sleeve coupling. It consists of a cylindrical sleeve with an internal diameter equal to the diameter of the shafts. The sleeve is connected to the shafts by a key that restricts their relative motion and prevents slippage. A few sleeve couplings also have threaded holes to prevent axial movement. This type of coupling is typically used for medium to light-duty torque.
Another type of mechanical coupling is a jaw coupling. It is used in motion control and general low-power transmission applications. This type of coupling does not require lubrication and is capable of accommodating angular misalignment. Unlike other types of couplings, the jaw coupling uses two hubs with intermeshing jaws. The jaw coupling’s spider is typically made of copper alloys. In addition, it is suitable for shock and vibration loads.
Mechanical couplings can be made from a variety of materials. One popular choice is rubber. The material can be natural or chloroprene. These materials are flexible and can tolerate slight misalignment.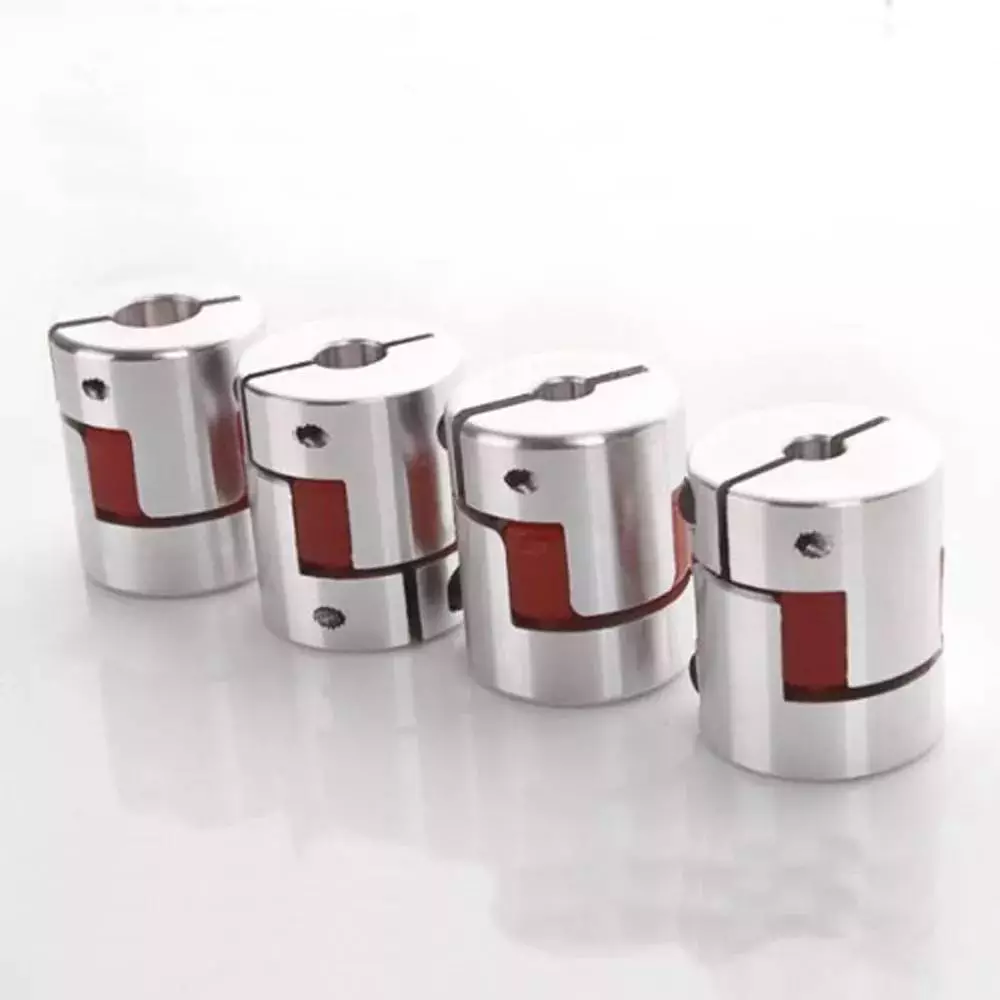
Electrical
Electrical coupling is the process in which a single electrical signal is transferred from a nerve cell to another. It occurs when electrical signals from two nerve cells interact with each other in a way similar to haptic transmission. This type of coupling can occur on its own or in combination with electrotonic coupling in gap junctions.
Electrical coupling is often associated with oscillatory behavior of neurons. The mechanism of electrical coupling is complex and is studied mathematically to understand its effect on oscillatory neuron networks. For example, electrical coupling can increase or decrease the frequency of an oscillator, depending on the state of the neuron coupled to it.
The site of coupling is usually the junction of opposing cell membranes. The cellular resistance and the coupling resistance are measured in voltage-clamp experiments. This type of coupling has a specific resistance of 100 O-cm. As a result, the coupling resistance varies with the frequency.
The authors of this study noted that electrotonic coupling depends on the ratio between the resistance of the nonjunctional membranes and the junctional membranes. The voltage attenuation technique helps reveal the differences in resistance and shunting through the intercellular medium. However, it is unclear whether electrotonic coupling is electrostatically mediated.
Electrical coupling has also been suggested to play a role in the intercellular transfer of information. There are many examples that support this theory. A message can be a distinct qualitative or quantitative signal, which results in a gradient in the cells. Although gap junctions are absent at many embryonic interaction sites, increasing evidence suggests a role in information transfer.
Flexible
When it comes to choosing the right Flexible Coupling, there are several factors that you should take into account. Among these factors is the backlash that can be caused by the movement of the coupling. The reason for this problem is the fact that couplings that do not have anti-fungal properties can be easily infected by mold. The best way to avoid this is to pay attention to the moisture content of the area where you are installing the coupling. By following these guidelines, you can ensure the best possible installation.
To ensure that you are getting the most out of your flexible couplings, you must consider their characteristics and how easy they are to install, assemble, and maintain. You should also look for elements that are field-replaceable. Another important factor is the coupling’s torsional rigidity. It should also be able to handle reactionary loads caused by misalignment.
Flexible couplings come in many different types. There are diaphragm and spiral couplings. These couplings allow for axial motion, angular misalignment, and parallel offset. They have one-piece construction and are made from stainless steel or aluminum. These couplings also offer high torsional stiffness, which is beneficial for applications requiring high torques.
Flexible couplings have several advantages over their rigid counterparts. They are designed to handle misalignments of up to seven degrees and 0.025 inches. These characteristics are important in motion control applications. Flexible couplings are also inexpensive, and they do not require maintenance.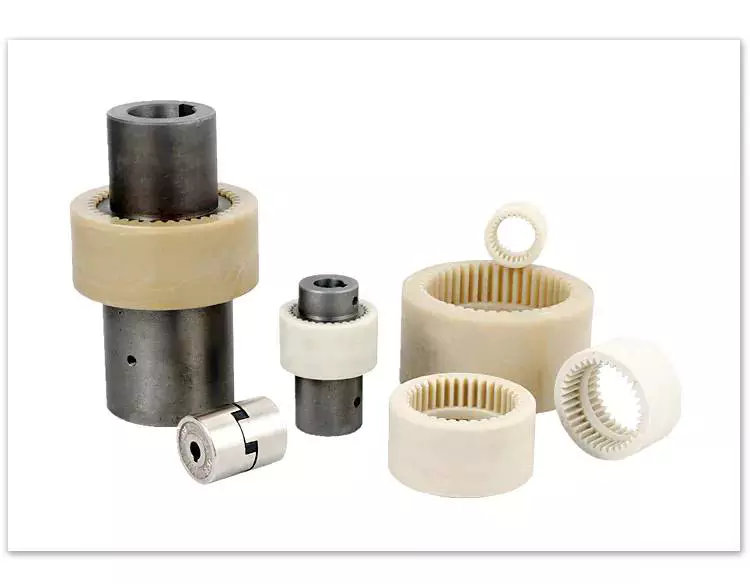
Beam
A beam coupling is a type of mechanical coupling, usually one solid piece, that connects two mechanical parts. Its performance is largely determined by the material used. Typical materials include stainless steel, aluminum, Delrin, and titanium. The beam coupling is rated for different speeds and torques. The coupling should be selected according to the application. In addition to the material, the application should also consider the speed and torque of the system.
There are two main types of beam couplings. The first is the helical beam coupling, which has a continuous multi spiral cut. This type of coupling offers a high degree of flexibility and compensates for a high degree of misalignment. The second type of beam coupling is the helical shaft coupling, which has a low torsional stiffness, which makes it ideal for small torque applications.
Another type of beam coupling is the multiple beam design, which combines two beams. It allows for more tolerance in manufacturing and installation and protects expensive components from excessive bearing loads. It also helps keep beams shorter than a single beam coupling. This type of coupling also enables a higher torque capacity and torsional stiffness.
Beam couplings can be manufactured with different materials, including stainless steel and aluminum. The “A” series is available in aluminum and stainless steel and is ideal for general-purpose and light-duty applications. It is also economical and durable. This type of coupling can also be used with low torque pumps or encoder/resolver systems.
Pin & bush
The Pin & bush coupling is a versatile, general-purpose coupling with high tensile bolts and rubber bushes. It can tolerate a wide range of operating temperatures and is suitable for use in oil and water-resistance applications. Its unique design enables it to be used in either direction. In addition, it requires no lubrication.
The pin bush coupling is a fail-safe coupling with a long service life and is used for high-torque applications. It provides torsional flexibility and dampens shocks, making it a flexible coupling that protects equipment and reduces maintenance costs. Its hubs are forged from graded cast iron for strength and durability. Besides, the coupling’s elastomer elements reduce vibration and impact loads. It also accommodates a misalignment of up to 0.5 degrees.
Pin & bush couplings are a popular choice for a variety of different applications. This coupling features a protective flange design that protects the coupling flange from wear and tear. The coupling nut is secured to one flange, while a rubber or leather bush sits between the other flange. Its unique design makes it ideal for use in applications where misalignment is a small factor. The rubber bushing also helps absorb vibration and shock.
Mesh tooth
Mesh tooth couplings are used to transfer torque between two shafts and reduce backlash. However, mesh tooth couplings have some limitations. One disadvantage is the break-away friction factor in the axial direction. This problem is caused by the high contact force between the tooth and gear mesh. This can cause unpredictable forces on the shafts.
In this paper, we present a FEM model for mesh tooth coupling. We first validate the mesh density. To do so, we compute the bolt stress as a uniaxial tensile during the tightening process. We used different mesh sizes and mesh density to validate our results.
The mesh stiffness of gear pairs is influenced by lead crown relief and misalignment. For example, if one tooth is positioned too far in the axis, the mesh stiffness will be decreased. A misaligned gear pair will lose torque capacity. A mesh tooth coupling can be lubricated with oil.
An ideal mesh tooth coupling has no gaps between the teeth, which reduces the risk of uneven wear. The coupling’s quality exposed fasteners include SAE Grade 5 bolts. It also offers corrosion resistance. The couplings are compatible with industrial environments. They also eliminate the need for selective assembly in sleeve couplings.

editor by czh 2022-11-26